U.S. maternal mortality rates are alarmingly on the rise, revealing a critical public health crisis that demands immediate attention. This issue encompasses pregnancy-related deaths that, shockingly, 80% are preventable with improved healthcare and support systems. The United States stands out among high-income nations for its disproportionately high maternal mortality, highlighting urgent maternal health issues, especially among marginalized racial groups. Recent studies indicate that cardiovascular disease has emerged as a leading cause of these fatalities, warranting a reconsideration of postpartum care practices. Addressing these preventable deaths requires a concerted effort to reform healthcare access, ensuring that every mother receives the care she needs throughout pregnancy and beyond.
The rising rates of maternal deaths in the United States reflect an alarming trend in pregnancy-related health outcomes. This emerging crisis signifies not just an issue of maternal health but also a broader systemic failure to protect vulnerable populations during and after childbirth. These pregnancy complications reportedly account for a significant percentage of fatalities that could be avoided with adequate intervention and support. Equally concerning is the relationship between pre-existing health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, and their impact on maternal well-being. A focused approach to improving postpartum care and reducing inequities in healthcare access is essential to reversing this troubling trajectory.
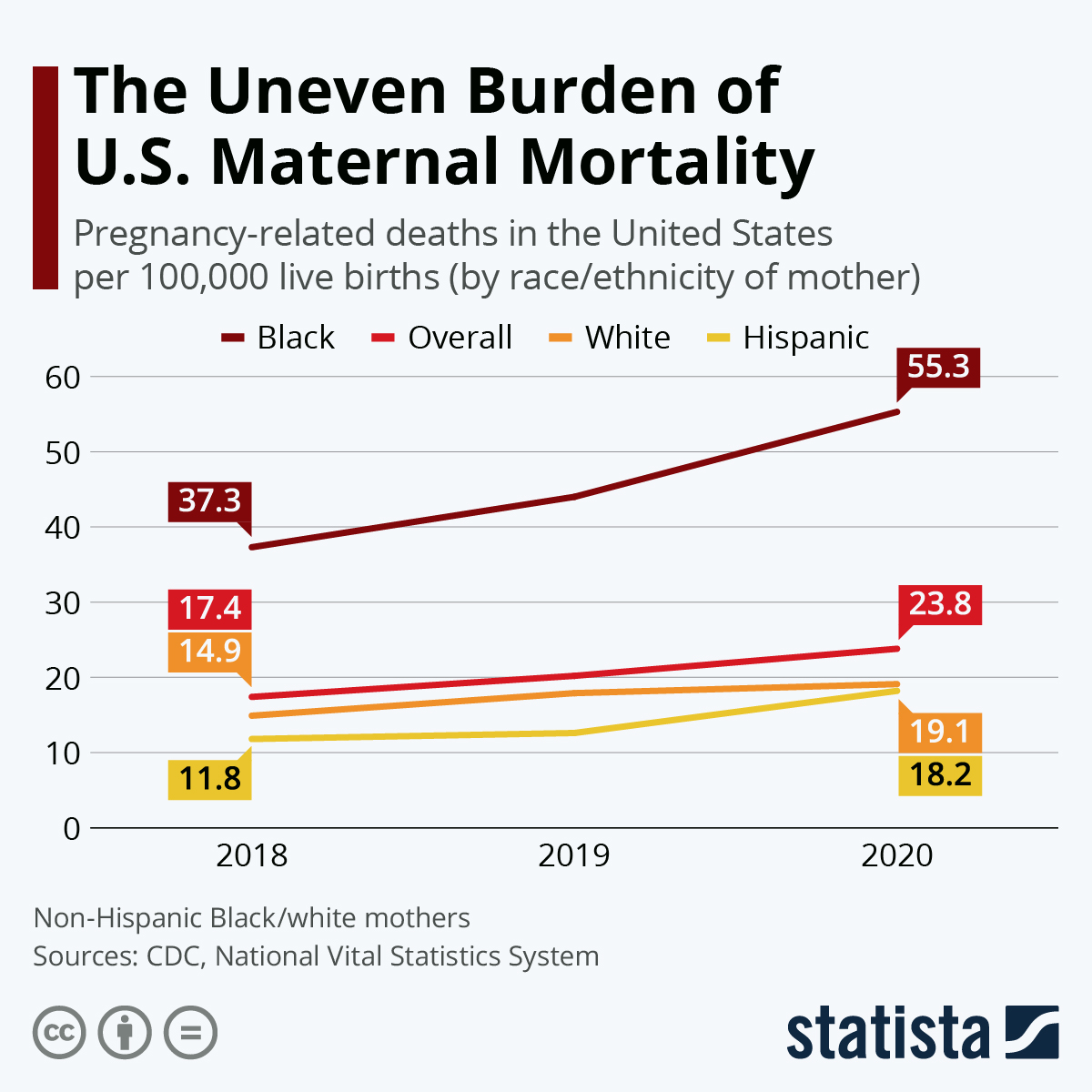
Understanding U.S. Maternal Mortality Trends
The U.S. continues to experience a troubling rise in maternal mortality, leading all high-income countries in this concerning statistic. Recent studies indicate that over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, yet systemic issues within the healthcare system exacerbate the problem. Factors such as a fragmented healthcare structure, lack of equitable policies, and insufficient access to quality care disproportionately affect marginalized communities, leading to alarming disparities across racial and ethnic lines.
Between 2018 and 2022, maternal deaths in the U.S. increased, with 2021 showing the steepest rise due to the COVID-19 pandemic’s impact. This spike in mortality rates highlights the need for urgent reform, particularly in prenatal and postpartum care. By implementing comprehensive monitoring and improving access to healthcare resources, the U.S. can work toward reducing these preventable deaths and ensuring safer pregnancies for all women.
Statistical reports reveal stark inequalities; for instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate nearly four times higher than that of their white counterparts. This situation underscores an urgent necessity for targeted interventions aimed at enhancing maternal health and preventing deaths that could be avoided with proper care and support.
Addressing these disparities calls for multifaceted solutions, including improved public health infrastructure, enhanced maternal health education, and an emphasis on community-based care that accommodates the unique needs of all women across various demographics.
Linking Cardiovascular Disease and Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., accounting for a shocking 20 percent of these fatalities. This shift from hemorrhage as the primary cause emphasizes the growing prevalence of chronic conditions like hypertension among younger women. The increased rates of heart disease in pregnant individuals signal an alarming trend that necessitates immediate attention from healthcare professionals and policymakers alike.
The data indicate that pregnancy-related deaths have increased significantly among women aged 25 to 39 years. This highlights a dire need for improved screening and management of cardiovascular health during pregnancy. As more young women face chronic health issues, integrating cardiovascular care into maternal health practices can mitigate these risks and improve pregnancy outcomes. Ensuring continuous monitoring and treatment can greatly enhance safety for mothers and their children.
Healthcare systems must adapt to address these rising risks effectively. One approach is to incorporate cardiovascular screenings and education into prenatal visits, as well as to provide adequate support and resources for postpartum care, ensuring that women are not left to navigate their recovery alone. Comprehensive strategies that encompass both maternal health and chronic disease prevention are vital in reducing pregnancy-related mortality rates.
This focus on heart health not only targets immediate concerns but also emphasizes the importance of long-term wellness for women, promoting a continuous care model that extends well beyond the delivery room.
The Importance of Postpartum Care in Maternal Health
The postpartum period is a critical phase in maternal health, yet it often receives inadequate attention from healthcare providers. A striking finding of recent research is that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year after pregnancy, a period often overlooked in traditional maternal healthcare models. The lack of emphasis on postpartum care can contribute significantly to preventable deaths, especially when healthcare systems treat recovery as a short-term process.
Recognizing the postpartum phase as a continuum is vital for improving maternal health outcomes. This calls for an integrated approach, ensuring that women have access to ongoing support and care after childbirth. Improved postpartum care can include follow-up appointments, mental health screenings, and education about warning signs of complications. Such measures can substantially contribute to reducing maternal mortality rates by allowing healthcare providers to address emerging issues before they become life-threatening.
Healthcare policies must evolve to prioritize the continuum of care, addressing the complete spectrum from prenatal to postpartum. By enhancing systems to ensure comprehensive care in the months following delivery, healthcare systems can better safeguard the lives of new mothers and ultimately reduce the overall maternal mortality rate.
Empowering women with knowledge about their health during the postpartum period is equally important. Providing them with resources, access to specialists, and continuous monitoring can lead to healthier recoveries and better familial outcomes.
Addressing Racial Disparities in Maternal Mortality
Racial disparities in maternal mortality are a persistent issue in the United States, with women of color disproportionately affected by pregnancy-related deaths. The findings reveal that American Indian and Alaska Native women experience significantly higher mortality rates compared to white women. This trend demands urgent action from policymakers and healthcare providers to ensure that all women receive equitable maternal health care.
Factors contributing to these disparities include systemic bias, limited access to quality care, and socioeconomic barriers. To combat these challenges, targeted interventions must be implemented that focus on enhancing healthcare resources in underserved communities. By addressing the root causes of these disparities and ensuring that women of all backgrounds have access to comprehensive maternal care, we can work towards achieving better health outcomes for all mothers.
Moreover, educating healthcare providers about the impact of implicit bias can significantly improve patient experiences and trust in the healthcare system. Training programs that emphasize cultural competency and understanding diverse patient needs can foster a more inclusive atmosphere, ultimately leading to improved maternal health indicators.
The involvement of community organizations can further amplify efforts to reduce maternal mortality rates among marginalized groups. Collaborations focused on advocacy, education, and support can empower women of color to seek necessary care during and after pregnancy, bridging gaps in health disparities.
Innovative Solutions to Improve Maternal Health
As maternal mortality rates continue to rise in the U.S., innovative solutions must be prioritized to enhance the quality of care during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Investing in technology and data-driven approaches can help identify at-risk populations and provide tailored interventions to prevent preventable deaths. For example, utilizing telemedicine services can expand access to care for women living in maternity care deserts, ensuring timely support regardless of geographic location.
Additionally, developing comprehensive maternal health programs that incorporate mental health support and chronic disease management can significantly improve outcomes. By fostering a multidisciplinary approach to maternal care, healthcare providers can address the complex needs of expectant and new mothers, allowing for a holistic approach to treatment.
Community engagement also plays a critical role in driving innovations in maternal health. Establishing local support networks and peer-led initiatives can empower women to share their experiences and advocate for their health needs more effectively. These community-based programs can provide valuable resources, foster connections, and ultimately enhance the overall quality of maternal healthcare.
In order for these innovative solutions to be effective, they must be supported by comprehensive policy changes that prioritize maternal health, allocate necessary funding, and promote collaboration across various sectors. By taking collective action, the U.S. can work towards reducing maternal mortality and creating a safer environment for mothers and their children.
Enhancing Health Infrastructure for Maternal Safety
Strengthening the healthcare infrastructure is paramount to addressing the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Significant investment in public health systems is needed to ensure that monitoring, prevention, and treatment of pregnancy-related complications become a standard part of maternal care. This includes not only improving hospital facilities but also ensuring adequate training for healthcare providers to recognize and respond to the unique needs of pregnant women.
Creating robust data systems that accurately track and report maternal health outcomes can facilitate better understanding and intervention strategies. By establishing nationwide systems dedicated to maternal health data collection and analysis, states can implement evidence-based policies that target the specific needs of their populations.
Additionally, fostering collaborations between hospitals, community health organizations, and public health departments can lead to more cohesive strategies for addressing maternal health issues. By promoting inter-agency cooperation, healthcare systems can ensure that care is seamless and comprehensive, reducing the risk of pregnancy-related deaths and improving maternal health outcomes.
Investing in training programs that emphasize the importance of continuous care throughout pregnancy and into the postpartum period must also be part of this infrastructure overhaul. Healthcare providers need to have the resources and knowledge necessary to provide quality care and recognize the signs of potential complications early.
The Role of Public Health Initiatives in Maternal Care
Public health initiatives play a crucial role in addressing maternal mortality rates in the United States. Raising awareness about the importance of prenatal and postpartum care through targeted campaigns can empower women to seek necessary medical attention. Education programs must highlight the potential risks associated with pregnancy and emphasize the resources available for new mothers to receive comprehensive care.
Moreover, public health campaigns that focus on promoting healthy lifestyles prior to and during pregnancy can contribute to reducing chronic health conditions that lead to maternal deaths. Nutrition, exercise, and mental health support should be integral components of public health messaging directed at women of reproductive age. By addressing these factors holistically, we can positively influence maternal health outcomes.
Funding for public health initiatives must be prioritized as part of a national strategy to combat rising maternal mortality. Allocating resources toward research, community programs, and health education can pave the way for improved policies that support mothers and families during and after pregnancy. Collaborative efforts at various levels of government can ensure that maternal health remains a priority on the national agenda.
Public health initiatives must also address the need for culturally competent care options that cater to the unique needs of diverse populations. By fostering inclusive approaches to maternal health, we can work toward eliminating disparities and ensuring that all women receive the care they deserve.
Promoting Policy Changes to Support Maternal Health
Effective policy changes are essential to improving maternal health outcomes and reducing pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Current maternal health policies must be revisited and revised to address systemic inequities and ensure access to quality care for all women. Advocacy efforts should focus on increasing funding for maternal health programs, improving insurance coverage for postpartum care, and eliminating barriers to healthcare access.
Policymakers must acknowledge the importance of comprehensive maternal care that extends beyond the delivery of the baby to include follow-up services. Ensuring that insurance plans cover necessary postpartum check-ups, mental health screenings, and chronic disease management can significantly enhance the quality of care women receive after childbirth. Moreover, supporting policies that create incentives for hospitals to provide holistic maternal care can lead to widespread positive changes.
Collaboration between government entities, healthcare agencies, and community organizations is crucial for driving impactful changes. By working together, stakeholders can develop and promote evidence-based policies that are informed by the latest research and best practices in maternal health. Such collaborative efforts can lead to significant improvements in healthcare delivery and outcomes for mothers across the country.
Promoting transparency and accountability in maternal health services is also vital. Establishing clear metrics and benchmarks can help track progress and ensure that initiatives aimed at improving maternal health are yielding positive results. Policymakers should commit to regularly reviewing and revising maternal health policies to adapt to emerging data and evolving needs.
Advocating for Research in Maternal Health
Advocating for increased research into maternal health is fundamental to understanding and tackling the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. Research initiatives should focus on identifying risk factors, evaluating the effectiveness of existing maternal care programs, and developing innovative solutions to improve health outcomes. The data gleaned from this research will be instrumental in informing policy and guiding future interventions.
Furthermore, funding for maternal health research must be prioritized, particularly in the context of maternal mortality disparities across racial and ethnic groups. By dedicating resources to studies that explore the social determinants of health and the barriers faced by marginalized populations, researchers can provide valuable insights that drive changes in maternal healthcare practices.
Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and policymakers is essential to translate findings into actionable strategies. For instance, conducting studies that involve the voices of women affected by maternal health issues can illuminate the real-life implications of policy decisions and healthcare practices. This participatory approach can enhance the relevance and impact of research findings.
In conclusion, advancing maternal health research is pivotal to reducing preventable deaths and improving the overall quality of care for women. By fostering an environment that values and supports research initiatives, we can move toward a future where all women have access to safe and effective maternal healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the leading causes of U.S. maternal mortality?
Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of U.S. maternal mortality, accounting for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. This trend shows a significant shift from earlier causes such as hemorrhage, highlighting the importance of addressing maternal health issues like hypertension and other chronic conditions during pregnancy.
How can preventable deaths in U.S. maternal mortality be reduced?
To reduce preventable deaths in U.S. maternal mortality, it is essential to invest in quality prenatal care and extend postpartum care. By improving healthcare access and addressing disparities across states and racial groups, many of the 80% preventable pregnancy-related deaths could potentially be avoided.
Why is there a significant racial disparity in U.S. maternal mortality rates?
Racial disparities in U.S. maternal mortality rates are attributed to a variety of factors including inequitable healthcare access, systemic bias in medical treatment, and socioeconomic disparities. The study indicates that American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, highlighting urgent need for targeted interventions in maternal health.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is crucial in preventing maternal mortality, especially given that nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum. Comprehensive care during this period can address ongoing health issues and improve recovery outcomes.
How does chronic disease impact U.S. maternal mortality rates?
The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, especially cardiovascular conditions, among reproductive-age individuals is significantly impacting U.S. maternal mortality rates. More young women are presenting with hypertension and other related disorders during pregnancy, contributing to the overall rise in these preventable deaths.
What is the trend of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. from 2018 to 2022?
Between 2018 and 2022, pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. rose from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, indicating a troubling upward trend, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. This data highlights the urgent need for systemic changes in maternal healthcare.
Why is it important to include late maternal deaths in discussions of U.S. maternal mortality?
Including late maternal deaths, which occur up to one year postpartum, is vital as it reflects the continuum of maternal health issues beyond the immediate postpartum period. Recognizing and addressing these deaths can lead to better healthcare systems and targeted interventions to improve outcomes for new mothers.
What should be prioritized to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
Improving maternal health outcomes in the U.S. requires prioritization of public health infrastructure, increased funding for research, and development of quality care programs during pregnancy and postpartum. Understanding state-level variations and addressing policy differences is also crucial for implementing effective solutions.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries, which have been increasing since 2018. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Disparities in Mortality by Race | American Indian and Alaska Native women experienced the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in mortality rates was noted in 2021, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Decline in Postpartum Care | Late maternal deaths accounted for almost a third of deaths, indicating a need for better postpartum care. |
| Need for Better Policies | State variability in mortality rates suggests a need for more equitable healthcare policies. |
| Chronic Health Conditions | The rise in cardiovascular disease is tipping the causes of maternal mortality, highlighting underlying health issues. |
| Investment in Healthcare | There is a critical need for better investment in public health infrastructure and maternal healthcare quality. |
Summary
U.S. maternal mortality rates are alarmingly high and continue to rise, indicating a serious public health crisis. The increase, particularly among marginalized groups, highlights significant disparities and underscores the urgent need for systemic reforms in prenatal and postpartum care. With over 80% of these deaths considered preventable, comprehensive healthcare policies and improved access to care are essential in addressing this tragic issue.