Bile imbalance liver cancer represents a critical area of study in understanding how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to severe liver diseases, such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent type of liver cancer. Research has unveiled a vital molecular switch that impacts bile acids, and in doing so, offers hope for liver cancer treatment strategies. These findings emphasize the importance of the YAP FXR connection, a pivotal pathway governing bile metabolism and its implications for liver health. As part of ongoing liver disease research, the discovery highlights an overproduction of bile acids, leading to liver inflammation and eventually cancer. By addressing bile imbalance, scientists are paving the way for innovative therapeutic interventions to combat the rise of liver cancer globally.
The phenomenon of bile imbalance and its correlation with liver cancer encompasses a growing body of knowledge surrounding hepatic disorders. This exploration into bile acid dysregulation sheds light on potential pathways that contribute to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, a major liver malignancy. Noteworthy insights into the YAP and FXR pathways allow researchers to uncover the complexities of bile metabolism. As scientists continue to delve into liver disease dynamics, understanding the role of bile acids becomes crucial in devising effective liver cancer treatment options. Navigating these intricate connections opens doors to innovative solutions tailored to disrupt cancer progression and enhance patient outcomes.
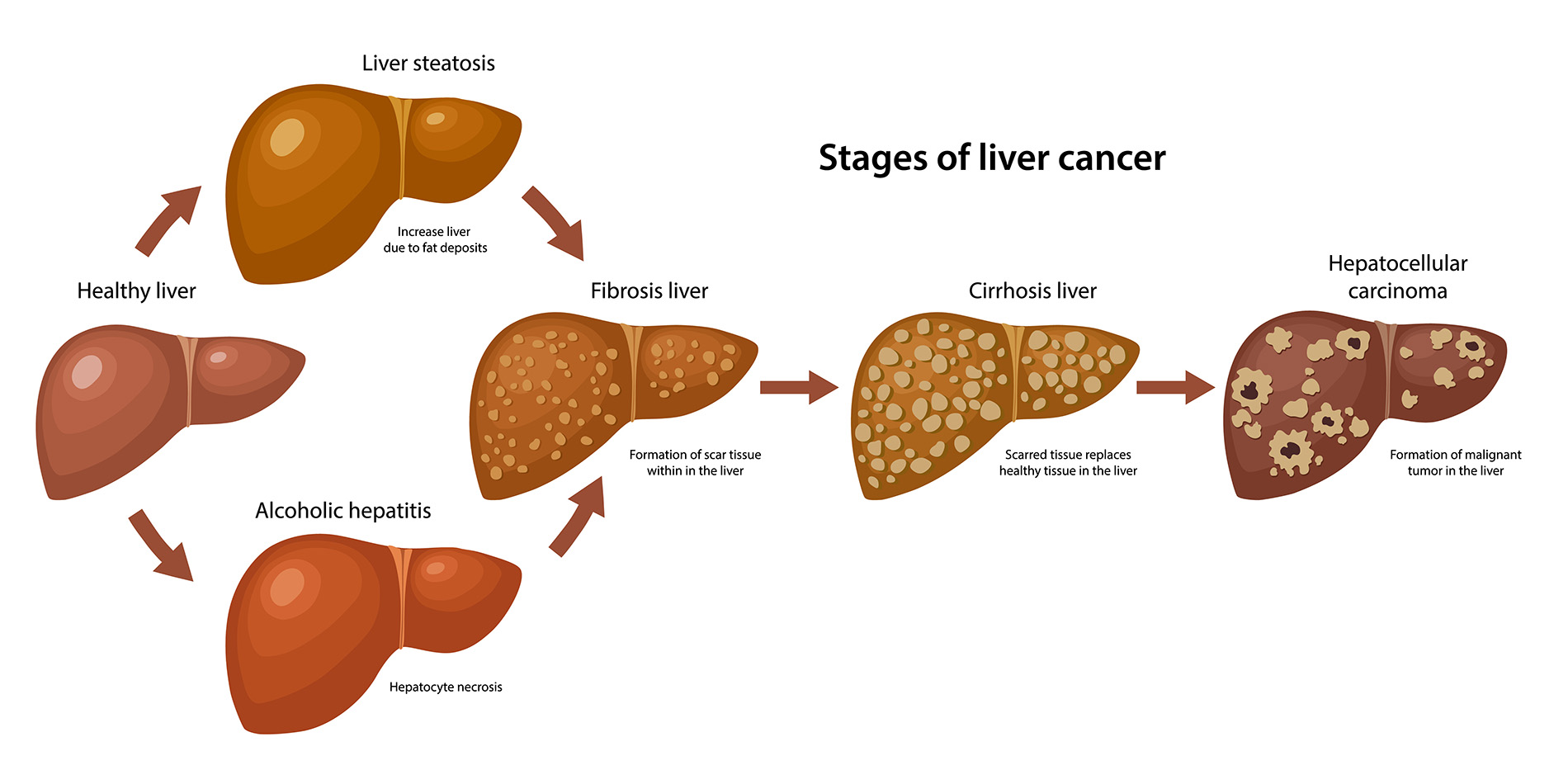
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Role in Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance is becoming increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver’s role in producing bile acids, essential for fat digestion, extends beyond digestion as these substances also influence diverse metabolic processes. Disruption of bile acid homeostasis can initiate a cascade of adverse effects, including inflammation and fibrosis, which inevitably link to liver malignancies. Recent findings suggest that monitoring bile acid levels could serve as a potential early detection method for liver diseases, offering insights into patient management strategies.
Research conducted by Yang and her team highlights an essential pathway involving the YAP protein and FXR receptor in regulating bile acid metabolism. Their groundbreaking discovery that YAP acts as a repressor of FXR unveils a mechanism whereby an overproduction of bile acids occurs, leading to liver damage and enhanced cancer risk. By focusing on the bile acid regulatory dysfunction, this line of research opens the door to innovative treatment modalities that may leverage the FXR pathway, potentially changing the landscape of liver cancer treatment.
The Connection Between Bile Acids and Liver Disease
Bile acids are not only critical for digestion but also play a pivotal role in metabolic regulation and liver health. Studies indicate that an imbalance in bile acids can be a critical contributor to several liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. By interfering with the normal signaling pathways that regulate bile production and excretion, such imbalances may lead to inflammation and fibrosis, both of which are precursors to cancerous transformations in the liver. Understanding this relationship is vital for the development of targeted liver cancer interventions.
Recent advancements in liver disease research underscore the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis as a preventive strategy against liver cancer. Researchers are investigating various pharmacological approaches to restore balance to bile acid levels, potentially reducing the incidence of liver disease progression. As the understanding of bile acids continues to evolve, it is becoming clear that strategies to modulate bile metabolism could provide new avenues for not only treating liver diseases but also improving overall liver function.
YAP and FXR: Targeting the Molecular Pathway for Liver Cancer Treatment
The Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has garnered attention for its critical role in cancer biology, especially concerning liver cancer. The intriguing connection between YAP and FXR, as highlighted in recent studies, presents a novel target for therapeutic intervention. By modulating this pathway, researchers aim to inhibit YAP’s repressive effects on bile acid metabolism, ultimately fostering a healthier bile acid profile that may diminish cancer risk. Clarifying this relationship represents a significant step forward in liver cancer treatment, providing potential new drug targets.
Moreover, targeting the YAP-FXR connection does not solely focus on inhibiting tumor growth; it also encompasses enhancing bile acid metabolism and improving liver function. By activating FXR or promoting bile acid export, current studies show promising results in reducing liver damage. This dual approach emphasizes not just on combating existing cancer but also on preventing its development, ultimately aiming to improve patient outcomes in hepatic diseases.
Research Innovations in Liver Disease and Cancer
Innovative research initiatives are continuously shedding light on the complex mechanisms underlying liver diseases and cancer. The dynamic work of researchers like Yingzi Yang, who utilize molecular and cellular biology techniques, is pivotal in unraveling the intricate pathways that govern liver health. By studying the roles of signaling molecules, such as YAP and FXR, scientists are better understanding how disruption in these pathways can lead to conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma. This insight paves the way for the development of novel liver cancer treatments.
Furthermore, leveraging findings from cutting-edge studies not only enhances our comprehension of liver disease mechanisms but also serves as a foundation for clinical applications. Collaborative research efforts will likely focus on the translational aspect, moving discoveries from the lab to the clinic. As we unravel the complexities of liver disease, the potential for breakthrough therapies targeting bile acid imbalances, signaling pathways, and metabolic processes grows, revolutionizing liver cancer treatment.
The Future of Liver Cancer Treatments Informed by Bile Research
As molecular biology advances, the future of liver cancer treatments looks promising, particularly through innovative research focused on bile acids. Understanding the intricate roles these compounds play in liver health and disease could lead to breakthroughs in intervention strategies, especially in treating hepatocellular carcinoma. By targeting the mechanisms behind bile imbalance, scientists can develop therapies that not only address symptoms but also tackle the root causes of liver cancer, potentially reducing overall incidence rates in at-risk populations.
Integrating findings from studies unraveling the YAP-FXR connection allows researchers to explore pharmacological strategies aimed at restoring bile acid homeostasis. With ongoing advancements in liver disease research, the next generation of liver cancer treatments may rely heavily on modulating bile acid signaling pathways. By investing in this line of inquiry, we can not only enhance current therapeutic options but also pave the way for preventative measures in liver health, ultimately reducing the burden of liver-related diseases.
The Impact of Bile Acids on Liver Health and Disease Progression
The relationship between bile acids and liver health is intricate, impacting both homeostasis and disease progression. Anomalies in bile acid levels can disrupt various metabolic processes, leading to conditions like liver inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding bile acids’ roles can illuminate why certain individuals develop liver diseases while others with similar risk factors do not. This knowledge will be instrumental in tailoring individualized preventive strategies and treatments.
Research has shown that leveraging the role of bile acids can also inform dietary and lifestyle interventions to promote liver health. Nutritional strategies that optimize bile acid production and excretion may offer additional support to patients at risk for liver cancer. This holistic approach to managing liver health, which includes understanding the complex interplay of bile acids, represents a comprehensive strategy towards finding effective treatments for liver diseases.
Molecular Pathways of Bile Acids in Liver Cancer Development
Diving deeper into molecular pathways associated with bile acids reveals critical insights into liver cancer development. Specifically, the interplay between bile acids, YAP, and FXR illustrates how molecular abnormalities can catalyze the transition from liver health to malignancy. Delineating these pathways offers a clearer understanding of how disruptions can lead to rapid disease progression, which is vital in identifying high-risk patients and timing interventions accordingly.
Moreover, targeting these specific molecular pathways opens up a realm of possibilities for innovative treatment strategies. By understanding the mechanisms behind bile acid regulation, researchers are exploring therapeutic agents that can restore balance within these pathways, ultimately providing new hope for patients facing liver cancer. The intersection of molecular biology and clinical applications in this domain is an exciting frontier in liver disease research.
Exploring Innovative Therapies for Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer
In light of recent findings on the impact of bile imbalances on liver cancer development, there is a surge of interest in exploring innovative therapeutic approaches. Therapies designed to enhance bile acid regulation—either by activating FXR or promoting bile acid excretion—are emerging as potential strategies to prevent or slow down the progression of liver cancer. The key to these interventions lies in developing drugs that can effectively target these pathways.
The promise of innovative therapies rests on further understanding bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver disease treatment. Ongoing research will likely continue to unveil new targets and pathways, driven by the urgent need to manage liver cancer effectively. As new therapeutic avenues emerge, the potential for improving patient outcomes becomes increasingly attainable, setting a new standard in the fight against liver cancer.
The Role of Bile Acids in Metabolic Health and Liver Cancer Prevention
Bile acids serve essential functions beyond digestion, playing a crucial role in maintaining metabolic health. Imbalances in bile acid concentrations can lead to broader metabolic dysregulation, linking them with the development of liver cancer. Understanding these associations highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy metabolic state as a strategy to prevent liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma.
Recent studies have also begun to explore the potential of bile acids as biomarkers for metabolic conditions. By assessing bile acid profiles, researchers could identify at-risk individuals earlier and implement preventive strategies. This emerging field of study underscores the importance of integrated approaches focused on bile acid homeostasis to mitigate the impact of liver disease and potentially prevent the onset of liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is bile imbalance related to liver cancer?
Bile imbalance plays a critical role in the development of liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). An overproduction of bile acids caused by a disruption in bile acid regulation can lead to liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately trigger liver cancer.
What is the role of bile acids in liver disease research?
Bile acids are essential in liver disease research as they regulate metabolic processes and visceral homeostasis. Abnormalities in bile acid metabolism have been linked to various liver conditions, including cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma, making them a key focus for potential therapeutic interventions.
What is the Hippo/YAP connection to bile imbalance and liver cancer treatment?
The Hippo/YAP pathway significantly influences bile acid metabolism and liver cancer development. The research indicates that YAP, when activated, represses FXR, a crucial bile acid sensor, leading to bile imbalance. Targeting this pathway could pave the way for innovative liver cancer treatment strategies.
Can enhancing FXR function help in liver cancer treatment?
Yes, enhancing FXR function may help combat bile imbalance and associated liver cancer. Researchers have found that stimulating FXR can counteract the negative effects of YAP activation, potentially reducing liver inflammation and preventing tumor progression.
What is the significance of the YAP FXR interaction in hepatocellular carcinoma?
The interaction between YAP and FXR is significant in hepatocellular carcinoma as it reveals how YAP inhibits FXR’s role in bile acid homeostasis. Understanding this connection opens new avenues for liver cancer research and potential pharmacological treatments.
What preventive measures can be taken against bile imbalance leading to liver cancer?
Preventive measures against bile imbalance include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring liver health, managing chronic liver diseases, and potentially developing interventions that target bile acid production and metabolism to reduce the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
How does inflammation relate to bile imbalance and liver cancer risk?
Inflammation resulting from bile imbalance can lead to tissue damage, fibrosis, and ultimately increase the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Managing inflammation through lifestyle changes or medical treatments may help mitigate this cancer risk.
What are the latest findings on bile imbalance and liver cancer treatments?
Recent studies have identified novel molecular targets, such as FXR and YAP, that are pivotal in regulating bile balance and preventing liver cancer development. These findings suggest pharmacological approaches that enhance FXR function or inhibit YAP’s activity could provide effective liver cancer therapies.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Focus | Identifying the link between bile imbalance and liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Role of Bile | Bile aids in fat digestion and has hormone-like functions affecting metabolic processes. |
| Key Molecular Switch | The study identifies YAP as a critical regulator that affects bile acid metabolism. |
| Impact of YAP Activation | YAP paralyzes FXR, leading to bile acid overproduction, liver inflammation, and cancer progression. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s repressive activity or enhancing FXR function shows promise in treatment interventions. |
| Research Implications | Enhancing understanding of YAP’s role may lead to pharmacological solutions for liver cancer. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is a critical health issue that reveals the intricate relationship between bile acids and liver disease. Recent research highlights a key molecular switch, YAP, which disrupts bile acid metabolism, leading to hepatocellular carcinoma. By addressing this imbalance, potential therapeutic strategies could be developed, offering hope for effective treatment options against this prevalent form of liver cancer.